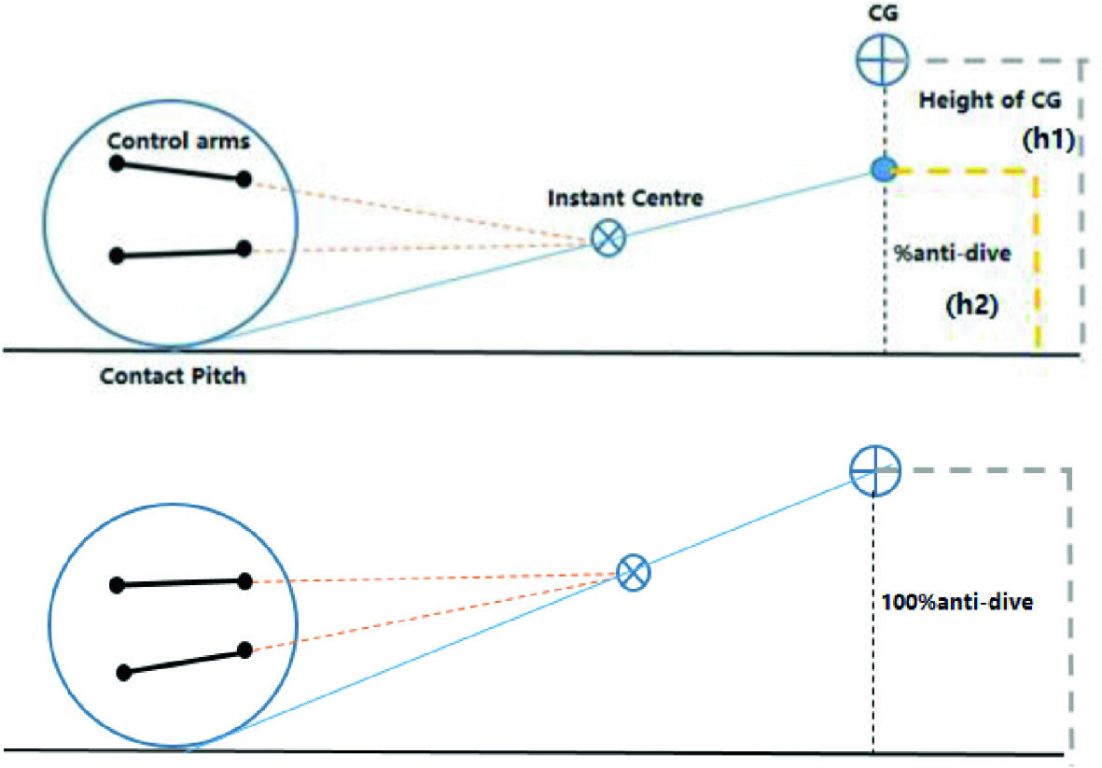
Rear Suspension Anti Squat . As you accelerate and the bike moves forward, the rider’s weight moves rearward causing the suspension to compress or squat. The biomechanics of pedaling (downward force of legs) also produce a downward force causing the suspension to compress or squat. — anti squat suspension can help manage these weight shifts, improving your traction and control even on rough terrain. During deceleration under braking, inertial forces generate a pitching moment (torque) around the centre of mass (com) and the body.
from www.newsf1.it
As you accelerate and the bike moves forward, the rider’s weight moves rearward causing the suspension to compress or squat. During deceleration under braking, inertial forces generate a pitching moment (torque) around the centre of mass (com) and the body. The biomechanics of pedaling (downward force of legs) also produce a downward force causing the suspension to compress or squat. — anti squat suspension can help manage these weight shifts, improving your traction and control even on rough terrain.
F1 Parametri di assetto. Come vengono influenzati dalla variazione
Rear Suspension Anti Squat During deceleration under braking, inertial forces generate a pitching moment (torque) around the centre of mass (com) and the body. As you accelerate and the bike moves forward, the rider’s weight moves rearward causing the suspension to compress or squat. — anti squat suspension can help manage these weight shifts, improving your traction and control even on rough terrain. During deceleration under braking, inertial forces generate a pitching moment (torque) around the centre of mass (com) and the body. The biomechanics of pedaling (downward force of legs) also produce a downward force causing the suspension to compress or squat.
From www.youtube.com
Understanding AntiSquat (MTB rear suspension Ep.11) YouTube Rear Suspension Anti Squat As you accelerate and the bike moves forward, the rider’s weight moves rearward causing the suspension to compress or squat. The biomechanics of pedaling (downward force of legs) also produce a downward force causing the suspension to compress or squat. During deceleration under braking, inertial forces generate a pitching moment (torque) around the centre of mass (com) and the body.. Rear Suspension Anti Squat.
From www.associatedelectrics.com
Rear Suspension Mounts, 3 deg. toe, 0 deg. antisquat Associated Rear Suspension Anti Squat — anti squat suspension can help manage these weight shifts, improving your traction and control even on rough terrain. During deceleration under braking, inertial forces generate a pitching moment (torque) around the centre of mass (com) and the body. As you accelerate and the bike moves forward, the rider’s weight moves rearward causing the suspension to compress or squat.. Rear Suspension Anti Squat.
From www.jalopyjournal.com
Rear Suspension Satchel 4 Link Suspension was my choice because "with a Rear Suspension Anti Squat — anti squat suspension can help manage these weight shifts, improving your traction and control even on rough terrain. During deceleration under braking, inertial forces generate a pitching moment (torque) around the centre of mass (com) and the body. The biomechanics of pedaling (downward force of legs) also produce a downward force causing the suspension to compress or squat.. Rear Suspension Anti Squat.
From forums.13x.com
Gearing vs antisquat vs everything else 13x Forums Rear Suspension Anti Squat During deceleration under braking, inertial forces generate a pitching moment (torque) around the centre of mass (com) and the body. As you accelerate and the bike moves forward, the rider’s weight moves rearward causing the suspension to compress or squat. The biomechanics of pedaling (downward force of legs) also produce a downward force causing the suspension to compress or squat.. Rear Suspension Anti Squat.
From www.hakon.com.au
Rear Trailing Arm Anti Squat Correction Hakon Suspension Melbourne Rear Suspension Anti Squat The biomechanics of pedaling (downward force of legs) also produce a downward force causing the suspension to compress or squat. As you accelerate and the bike moves forward, the rider’s weight moves rearward causing the suspension to compress or squat. — anti squat suspension can help manage these weight shifts, improving your traction and control even on rough terrain.. Rear Suspension Anti Squat.
From www.youtube.com
ANTISQUAT // ANTILIFT TRAILING ARMS!! Verkline suspension is Rear Suspension Anti Squat During deceleration under braking, inertial forces generate a pitching moment (torque) around the centre of mass (com) and the body. — anti squat suspension can help manage these weight shifts, improving your traction and control even on rough terrain. As you accelerate and the bike moves forward, the rider’s weight moves rearward causing the suspension to compress or squat.. Rear Suspension Anti Squat.
From www.associatedelectrics.com
Rear Suspension Mounts, 3 deg. toe, 3 deg. antisquat Associated Rear Suspension Anti Squat The biomechanics of pedaling (downward force of legs) also produce a downward force causing the suspension to compress or squat. As you accelerate and the bike moves forward, the rider’s weight moves rearward causing the suspension to compress or squat. During deceleration under braking, inertial forces generate a pitching moment (torque) around the centre of mass (com) and the body.. Rear Suspension Anti Squat.
From toprolls.com.tr
Traxxas Rear AntiSquat Suspension Hinge Pin Mount Set Fiyat ve Rear Suspension Anti Squat — anti squat suspension can help manage these weight shifts, improving your traction and control even on rough terrain. The biomechanics of pedaling (downward force of legs) also produce a downward force causing the suspension to compress or squat. During deceleration under braking, inertial forces generate a pitching moment (torque) around the centre of mass (com) and the body.. Rear Suspension Anti Squat.
From www.camaroz28.com
how can you find the instant center on a torque arm rear suspension Rear Suspension Anti Squat — anti squat suspension can help manage these weight shifts, improving your traction and control even on rough terrain. The biomechanics of pedaling (downward force of legs) also produce a downward force causing the suspension to compress or squat. As you accelerate and the bike moves forward, the rider’s weight moves rearward causing the suspension to compress or squat.. Rear Suspension Anti Squat.
From www.raceanalysis.it
F1 A deep dive into the antidive! How F1 “antidive” and “antisquat Rear Suspension Anti Squat During deceleration under braking, inertial forces generate a pitching moment (torque) around the centre of mass (com) and the body. As you accelerate and the bike moves forward, the rider’s weight moves rearward causing the suspension to compress or squat. The biomechanics of pedaling (downward force of legs) also produce a downward force causing the suspension to compress or squat.. Rear Suspension Anti Squat.
From www.huxracing.com
SW20 Antisquat Bar Rear Suspension Anti Squat The biomechanics of pedaling (downward force of legs) also produce a downward force causing the suspension to compress or squat. During deceleration under braking, inertial forces generate a pitching moment (torque) around the centre of mass (com) and the body. — anti squat suspension can help manage these weight shifts, improving your traction and control even on rough terrain.. Rear Suspension Anti Squat.
From www.youtube.com
AntiSquat Suspension Geometry Explained YouTube Rear Suspension Anti Squat As you accelerate and the bike moves forward, the rider’s weight moves rearward causing the suspension to compress or squat. — anti squat suspension can help manage these weight shifts, improving your traction and control even on rough terrain. The biomechanics of pedaling (downward force of legs) also produce a downward force causing the suspension to compress or squat.. Rear Suspension Anti Squat.
From www.stangtv.com
S197 Mustang, Instant Center, Anti Squat, Suspension Rear Suspension Anti Squat The biomechanics of pedaling (downward force of legs) also produce a downward force causing the suspension to compress or squat. As you accelerate and the bike moves forward, the rider’s weight moves rearward causing the suspension to compress or squat. — anti squat suspension can help manage these weight shifts, improving your traction and control even on rough terrain.. Rear Suspension Anti Squat.
From www.amainhobbies.com
Team Associated Rear Suspension Mount Set (3° Toe/0° AntiSquat Rear Suspension Anti Squat — anti squat suspension can help manage these weight shifts, improving your traction and control even on rough terrain. The biomechanics of pedaling (downward force of legs) also produce a downward force causing the suspension to compress or squat. During deceleration under braking, inertial forces generate a pitching moment (torque) around the centre of mass (com) and the body.. Rear Suspension Anti Squat.
From www.benzworld.org
Rear suspension anti squat bracket replacement MercedesBenz Forum Rear Suspension Anti Squat — anti squat suspension can help manage these weight shifts, improving your traction and control even on rough terrain. The biomechanics of pedaling (downward force of legs) also produce a downward force causing the suspension to compress or squat. During deceleration under braking, inertial forces generate a pitching moment (torque) around the centre of mass (com) and the body.. Rear Suspension Anti Squat.
From community.cartalk.com
Rear suspension geometries, can they be combined? General Discussion Rear Suspension Anti Squat As you accelerate and the bike moves forward, the rider’s weight moves rearward causing the suspension to compress or squat. — anti squat suspension can help manage these weight shifts, improving your traction and control even on rough terrain. During deceleration under braking, inertial forces generate a pitching moment (torque) around the centre of mass (com) and the body.. Rear Suspension Anti Squat.
From lowriders.ca
30390 Rear Anti Squat Bracket System Rear Suspension Anti Squat The biomechanics of pedaling (downward force of legs) also produce a downward force causing the suspension to compress or squat. As you accelerate and the bike moves forward, the rider’s weight moves rearward causing the suspension to compress or squat. During deceleration under braking, inertial forces generate a pitching moment (torque) around the centre of mass (com) and the body.. Rear Suspension Anti Squat.
From bloozeown.weebly.com
Blog Posts Rear Suspension Anti Squat The biomechanics of pedaling (downward force of legs) also produce a downward force causing the suspension to compress or squat. During deceleration under braking, inertial forces generate a pitching moment (torque) around the centre of mass (com) and the body. — anti squat suspension can help manage these weight shifts, improving your traction and control even on rough terrain.. Rear Suspension Anti Squat.